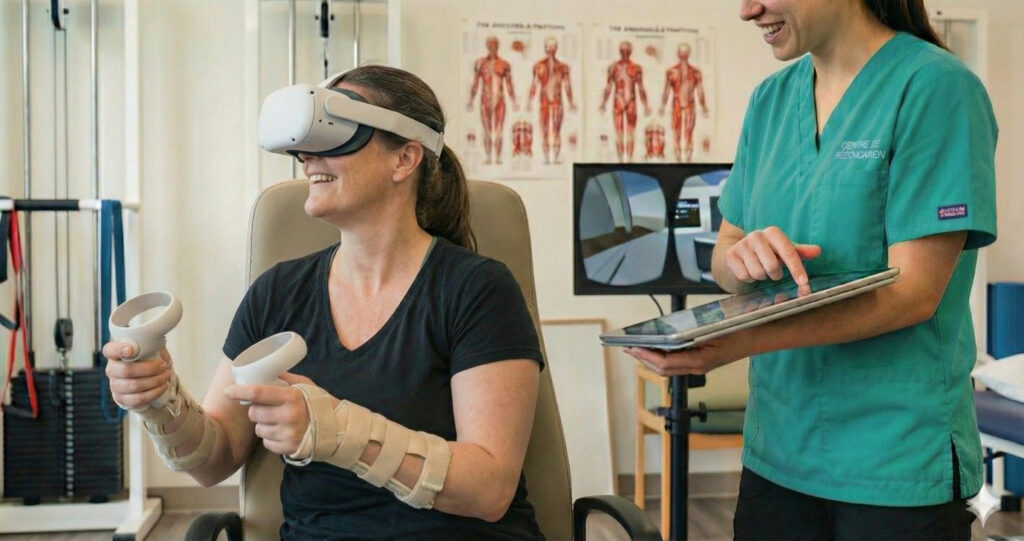
Introduction
Rehabilitation today faces major structural challenges: increasing demand for care, limited availability of healthcare professionals, reduced patient adherence, and unequal access to rehabilitation services in many regions.
In this context, virtual rehabilitation, based on virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, is emerging as a powerful and structured response.
This evolution is no longer experimental or purely technological. It is now recognized and framed by health authorities, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which formally considers AR and VR as technologies integrated into regulated medical devices.
What Is Virtual Rehabilitation?
Virtual rehabilitation refers to the use of immersive digital environments to support patients during functional, motor, or cognitive rehabilitation programs.
According to definitions used by the FDA:
- Virtual Reality (VR) places the patient in a fully immersive, computer-generated environment using a head-mounted display.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world.
- Together, these technologies fall under Extended Reality (XR).
When applied to healthcare, XR technologies are not entertainment tools. They form an active component of treatment, comparable to traditional rehabilitation devices.
How Does Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Work?
A virtual rehabilitation program combines several clinical and technological components:
- Therapeutic immersive scenarios designed around specific rehabilitation goals
- Motor and cognitive interactions performed by the patient in a controlled virtual environment
- Real-time feedback (visual, auditory, sometimes haptic) to reinforce motor learning
- Objective data collection (range of motion, accuracy, repetitions, reaction time) available to clinicians
These elements transform repetitive exercises into engaging experiences while preserving clinical rigor and traceability.
Clinical Applications of Virtual Rehabilitation
The FDA highlights multiple medical areas where AR and VR are already used as part of medical devices.
Neurological Rehabilitation
- Stroke
- Traumatic brain injury
- Neurodegenerative diseases
VR enables training of balance, coordination, motor control, and cognitive functions in safe, reproducible environments.
Orthopedic and Functional Rehabilitation
- Shoulder, knee, wrist rehabilitation
- Post-surgical recovery
Movements can be guided, measured, and adapted precisely to the patient’s abilities.
Cognitive and Behavioral Rehabilitation
- Attention disorders
- Anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder
The FDA explicitly references VR-based therapies in validated treatment protocols.
Remote Rehabilitation
Virtual rehabilitation supports tele-rehabilitation, allowing patients to continue therapy at home while remaining clinically supervised.
Benefits of Virtual Rehabilitation for Patients
Health authorities identify several key benefits:
- Improved treatment adherence through immersive and motivating experiences
- Active patient engagement, making patients participants rather than passive recipients
- Continuity of care, including outside clinical facilities
- Highly personalized therapy, adjusted to patient progress and limitations
These advantages are particularly relevant in aging populations and healthcare systems under pressure.
Benefits for Healthcare Professionals
For therapists and rehabilitation teams, virtual rehabilitation provides structural advantages:
- Objective monitoring of patient progress through automatically collected data
- Reduced administrative workload, especially for evaluation and reporting
- Advanced personalization of therapy programs
- Secure remote patient follow-up, without compromising clinical quality
The FDA emphasizes that AR/VR must be integrated as clinical tools, not consumer entertainment solutions.
Safety Considerations: What the FDA Emphasizes
The FDA also highlights important safety considerations associated with AR and VR medical devices:
- Cybersickness (nausea, dizziness, fatigue)
- Ergonomic and physical comfort of head-mounted devices
- Data security and patient privacy
- Clinical appropriateness of virtual content
These points reinforce the need for medical-grade solutions designed specifically for healthcare use.
Want to Learn More About FDA Safety Guidelines?
The FDA has published official infographics that clearly summarize the benefits, risks, and key questions patients and healthcare professionals should consider before using AR and VR medical devices.
Click here to view the FDA’s official AR/VR medical device infographics
These visuals provide a concise, regulator-backed overview that complements the clinical and technical information presented in this article.
Toward a Regulated and Recognized Virtual Rehabilitation Framework
The FDA publication marks a turning point:
AR and VR are no longer viewed as experimental technologies but as regulated components of medical devices, subject to safety, performance, and effectiveness requirements.
This regulatory recognition accelerates adoption of virtual rehabilitation across clinics, rehabilitation centers, and hospitals worldwide.
Virtual Rehabilitation and Clinical Innovation
In this evolving landscape, next-generation virtual rehabilitation platforms go beyond immersion alone by combining:
- Clinically designed immersive environments
- Tools that allow therapists to personalize and adapt exercises
- Clinical dashboards for decision-making and follow-up
- Secure tele-rehabilitation capabilities
This approach aligns technological innovation, regulatory expectations, and real-world clinical practice.
Conclusion
Virtual rehabilitation represents a major evolution in rehabilitation practices.
Supported by regulatory authorities such as the FDA, it combines clinical effectiveness, patient engagement, and optimization of healthcare professionals’ work.
As these technologies continue to mature and become regulated, virtual rehabilitation is positioned as a strategic pillar of modern rehabilitation care.